Plus everything you need to know for setting realistic SEO targets that are right for your business and you’ll feel good about
Sinking time, energy and budget into SEO marketing and seeing little or no return is depressing.
But it does happen, and when it fails it’s important to find out why.
I spend a lot of time doing this for companies who try SEO marketing and get frustrated because they can’t see a return.
And when that happens, they often lose sight of the value it can bring.
When I look at why it didn’t work, I usually find one of two things:
- there are no defined SEO goals
- the targets are unattainable.
Good SEO delivers results.
But there must be objectives and achievable goals.
So how do you create them? And what sort of SEO targets should you be setting?
Affordable digital marketing coaching you’ve been searching for. For online service-based small business owners who want more website traffic and more leads. Curious?
Start here: what to track and measure
Google Analytics (GA) reveals a lot about your business and how it’s performing online.
But while there are dozens of GA metrics you can look up, there are really only 7 measurements you must track as part of your SEO efforts.
- Organic search visits – how many people find your site by typing one of your keywords into the search engine (rather than coming from a paid ad).
- Search engine visibility – the percentage of time your website (or one of its pages) is visible in organic search results.
- New organic users – the number of people visiting your site for the first time.
- Referral traffic – people finding your website from other sources and sites, such as links on social media channels or backlinks.
- Keyword rankings – where your keyword is ranking in the search engine results.
- Keyword performance – the keyword that brings in the most organic traffic for your site.
- Click through rate (CTR) from search results – how many people click through to your site from organic search results.
These metrics can all be found in GA, and to track them I recommend setting up a spreadsheet so you can easily see the changes.
But how do you set goals for these metrics to know whether your SEO tweaks are having an effect?
Setting realistic SEO goals
Setting lofty goals you can’t meet will quickly kill your morale and tempt you to abandon your SEO plans.
I’m not saying you shouldn’t be ambitious.
But when measuring the value of SEO, your goals should always be attainable.
To find the right balance, look at the numbers in your business and how your site is currently performing.
When I’m setting SEO goals with my clients, I look at their total search volume, conversion rate, and average order amount (if they’re a commerce business).
Finding a realistic but progressive goal depends on whether there’s a known objective (e.g. the number of sales the business wants to make each month) or just a rough target (e.g. more site traffic to increase sales but the increase needed is unknown).
In both scenarios, setting good SEO goals means looking at the business’ current data and applying one of two formulas.
If you’re measuring leads, use the following.
Total search volume
x
67.6%
(percentage of clicks to the first five positions of organic search results)
x
Conversion rate
__________________________________________
Leads generated by organic search
If you’re measuring sales, you need this formula.
Total search volume
x
67.6%
x
Conversion rate
x
Average order amount
__________________________________________
Sales generated by organic search
By applying these formulas, my clients get a realistic SEO goal I can help them work towards.
Long- and short-term goals
Once you’ve put a number to your goal, the next step is to set a timeline.
Are you working with a long-term or short-term goal? Knowing this gives you a guide for when you can expect to see results.
SEO goals will be either a KPI or an OKR.
KPI stands for ‘key performance indicator’ while OKR is short for ‘objectives and key results.’
Here’s how Kameron Jenkins from botify.com sums up the difference between the two.
‘OKRs are centered on a specific goal you’d like to achieve in a period of time (e.g. a quarter), while KPIs typically measure ongoing work or processes that are already in place.’
An example of a short-term OKR could be getting X number of backlinks in Y months to achieve an outcome such as a percentage increase in referral traffic.
A longer-term KPI might be overall SEO site performance, an ongoing increase in leads, and so on.
A word on industry averages
Google Analytics and many SEO tools (e.g. SEMrush) offer industry-average SEO metrics.
While these are interesting to look at and be aware of, I don’t recommend them being the only source for setting your goals.
These metrics tend to include businesses of all shapes and sizes in your industry, including those that aren’t direct competitors.
So be aware of industry averages, but don’t be ruled by them.
Example SEO goals
Now that we’ve discussed what to track and measure, realistic goal figures, and long- or short-term goals, let’s look at examples of seven practical objectives you could set.
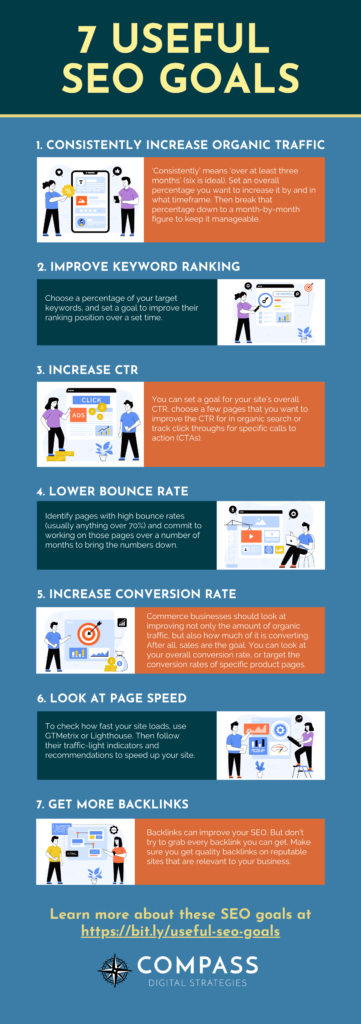
1. Consistently increase organic traffic
‘Consistently’ means ‘over at least three months’ (six is ideal).
Set an overall percentage you want to increase it by and in what timeframe.
Then break that percentage down to a month-by-month figure to keep it manageable.
Increase organic traffic by:
- revisiting your on-page SEO
- starting a blog (and refreshing poor-performing ones).
2. Improve keyword rankings
Choose a percentage of your target keywords, and set a goal to improve their ranking position over a set time.
Bear in mind that keyword difficulty is a factor in achieving this goal.
Improving the ranking of keywords that are difficult to rank for will take more time and effort.
Improve keyword rankings by:
- making sure the keyword is in (at least) the URL, the headline, and the body copy of the page.
3. Increase CTR
You can:
- set a goal for your site’s overall CTR
- choose a few pages that you want to improve the CTR for in organic search
- track click throughs for specific calls to action (CTAs).
Increase CTR by:
- updating your metadata to make the copy more enticing
- adding a clear CTA if there isn’t one already.
4. Lower the bounce rate
Bounce rate is when someone lands on your site, stays for a bit, and then leaves without taking any other action (e.g. going to another part of your site or buying something).
Identify pages with high bounce rates (usually anything over 70%) and commit to working on those pages over a number of months to bring the numbers down.
Lower the bounce rate by:
- revisiting the content on the page
- looking at where the page or content fits in the user journey
- checking site responsiveness, and how it works on different devices.
5. Increase conversion rate
Commerce businesses should look at improving not only the amount of organic traffic, but also how much of it is converting.
After all, sales are the goal.
You can look at your overall conversion rate, or target the conversion rates of specific product pages.
For example, seasonality might affect this goal and on which pages you want to see an increased conversion rate.
Increase conversion rate by:
- looking at your checkout process
- setting up abandoned basket reminders, incentives, and upsells
- tightening the copy on page to address audience pain points and discussing product benefits.
6. Look at page speed
Slow-loading pages are high bounce rate magnets.
While search engines don’t penalize slow sites exactly, they do favor faster-loading sites, and most likely rank them higher.
To check how fast your site loads, use GTMetrix or Lighthouse.
Then follow their traffic-light indicators and recommendations to speed up your site.
7. Get more backlinks
Backlinks can improve your SEO.
But don’t try to grab every backlink you can get.
Make sure you get quality backlinks on reputable sites that are relevant to your business.
Just keep in mind that building backlinks can be time consuming, especially if you’re a company of one and DIY-ing your SEO.
To set a realistic goal, consider how much time and resources you have available.
For example, do you have time to research, pitch, and write guest articles? Do you have the budget and workforce to outsource backlink building to speed the process up?
Get more backlinks by:
- pitching great content ideas to relevant sites
- setting up cross-brand marketing with likeminded businesses
- publishing amazing content on your own site that others will want to link to
- looking at sites already referring to you, and finding ways to expand that relationship.
SEO goals will change over time
Changing algorithms, business priorities, and customer needs all affect the SEO goals you set.
That means you’ll need to revisit your objectives from time to time.
For me and my clients, we do this annually for long-term goals and quarterly (or sometimes monthly) for smaller goals such as lowering bounce rates.
This keeps them relevant, and helps us make sure we’re hitting those targets.
This article has shown you what sort of SEO goals you can set for your business.
But if it still feels a bit much, my door is always open.
Contact me for a chat about your SEO strategy and tracking your business needs.
